Central Bank
Central Bank || Function of Central Bank:
Central bank is the most important bank of every country. Every country has its own central bank. It is the supreme bank of a country. It is regarded as the
Bank of the banks. It provides banking and financial services to government.
It formulates and implements monetary policy on behalf of the government.
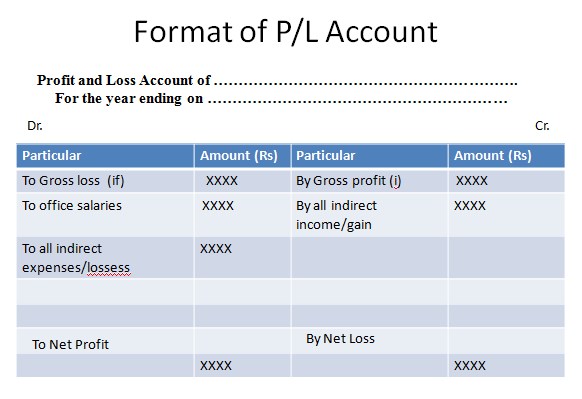
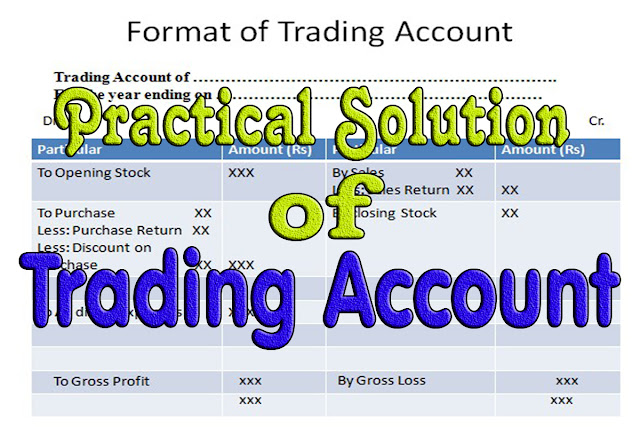
| Things to Remembers |
| Central bank is defined as the highest monetary authority of a country whose primary functions are related to issuance of notes and currencies, controlling other banking operation and making financial plans and policies for the economy of the nation. |
| According to Prof. Knet, "Central bank may be defined as an institution which is charged with the responsibility of managing, the expansion and construction of the volume of money in the interest of the public welfare." |
| The first Central Bank of the world was Reek Bank of Sweden which established in 1656 A.D. |
Nepal Rastrya Bank is the central bank of Nepal. It was established in 1956 (Baishak 14, 2013) under the Nepal Rastra Bank Act, 1955 (2012 B.S.). Reserve bank of India is the central bank of India, State Bank of Pakistan is the central bank of Pakistan, Bank of England is the central bank of England, Federal Reserve Bank is the central bank of United State and
Central Bank of China is the central bank of China.
Functions of Central bank:
The following are the functions of central bank;
- Issue of notes.
- Making financial plans and policies.
- Acts as the government bank.
- Acts as the bank of the other banks.
- Controlling credit creations.
- Central clearance
- Control of foreign exchange
- Development of banking system.
Very Important from the Examination View:
Define a central bank. Explain any eight functions of it.
Ans: Central bank is defined as the highest monetary authority of a country whose primary functions are related to issuance of notes and currencies, controlling other banking operation and making financial plans and policies for the economy of the nation.
According to Prof. Knet,
"Central bank may be defined as an institution which is charged with the responsibility of managing, the expansion and construction of the volume of money in the interest of the public welfare."
The following are the main functions of the central bank;
a) Issue of notes and currencies: Central bank has sole right to issue notes and currencies. It issues both paper notes and metal coins. Nepal Rastrya Bank issues paper notes of Re. 1, Rs. 2, Rs.5, Rs. 10, Rs. 20, Rs. 50, Rs. 100, Rs. 500 and Rs. 1000.
b) Making financial plans and policies: Central bank has right to make and control the monetary system of the countries. The structure of banking system and the necessary ordinances are made and circulated by this bank in order to have a watch over the operation of other
financial institutions in the country.
c) Acts as the government bank: The central bank acts as the agent of the government as it maintains the accounts of ministries, departments and operating level offices as well as other different government projects. It records government revenues and expenditure.
d) Acts as the bank of the other banks: Other banks are established and operated only after the permission and approval of the Central Bank. Central Bank is called the banker of all the banks because the government has given it a total authority to determine the types of banks that need to be established and to control them. It provides loan to the other banks.
e) Controlling Credit Creations: It controls the credit operation of commercial banks. Commercial banks expand credit which may increase inflationary pressure causing devaluation of money and price hikes, this situation is very terrible for the common people as well as government, therefore, the Central Bank applies some techniques of controlling the overflow of money by changing the rate of interest, issuing securities or laying restriction on commercial and other banks granting loans for a certain period of time.
f) Central Clearance: Central bank gives permission to establish other banks on the basis of cash reserve in the central bank. Such cash reserve makes easier to clear inter-bank transaction thus, central bank adjust the accounts of other banks by adjusting entries in their respective accounts.
g) Control of foreign exchange : Central bank works has the sole authority in foreign currency management. It regulates the supply of foreign currencies in national economy and maintains their exchange rate with home currency at proper level.
h) Development of Banking System: The government has a policy to support economic development through banking system. The central bank gives permission to individuals or institutions willing to establish bank only after depositing a certain amount of capital, as per the rules of the Central Bank. Central bank is involved in the development of banking system in a country. Further, It encourages the people for the banking habits.
| Some More Important Questions: |
Which is the central bank of Nepal.
Ans: Nepal Rastrya Bank is the Central Bank of Nepal. |
When was the Central Bank of Nepal established?
Ans: Central Bank of Nepal was established in 1956 (Baishak 14, 2013) under the Nepal Rastra Bank Act, 1955 (2012 B.S.). |
Which was the first central bank in the world?
Ans: The first Central Bank of the world was Reek Bank of Sweden. |
When was the first central bank in the world established?
Ans: The First Central Bank was established in 1656 A.D. |